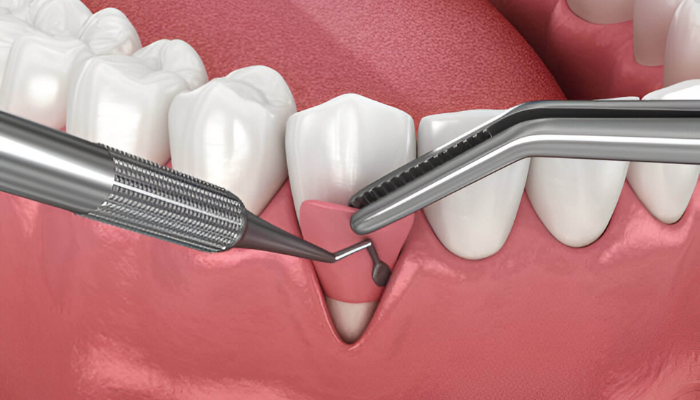
Gum grafting is a transformative procedure that restores receding gums, improves oral health, and enhances smiles. But many wonder, “When is it too late for gum grafting?” Understanding the timeline for gum grafting is crucial to preserving your oral health and avoiding complications. In this article, we’ll explore the factors that determine eligibility, discuss signs it may be too late, and offer advice on alternative solutions. If you’re worried about your gum health, this guide is your ultimate resource.
What Is Gum Grafting and Why Is It Necessary?
Gum grafting, also known as gingival grafting, is a surgical procedure designed to treat gum recession. Recession occurs when the gum tissue surrounding the teeth pulls back, exposing the roots and increasing sensitivity, risk of decay, and even tooth loss. A gum graft involves transplanting healthy tissue, often from the roof of the mouth or a donor source, to cover exposed roots and reinforce the gumline.
Not only does gum grafting improve aesthetics, but it also protects against further dental complications. Left untreated, gum recession can lead to severe issues, including bone loss and periodontal disease. This makes it imperative to address gum health early—before irreversible damage occurs.
While gum grafting is effective, timing plays a critical role. Early intervention is ideal, as advanced gum disease or insufficient healthy tissue can complicate the procedure. Understanding whether it’s too late for gum grafting depends on individual circumstances, which we’ll explore in detail below.
Signs It May Be Too Late for Gum Grafting
Knowing when gum grafting is no longer an option depends on the severity of gum and bone damage. Here are key indicators that it might be too late:
1. Advanced Bone Loss
Gum recession often coincides with bone loss, which provides essential support for teeth and gum tissue. If significant bone loss has occurred, gum grafting alone may not be effective. In such cases, additional procedures like bone grafting may be required before gum grafting can proceed.
2. Untreated Periodontal Disease
Periodontal disease is a leading cause of gum recession. If the disease progresses unchecked, it can cause irreversible damage to the gums and underlying bone. Advanced periodontal disease can render gum grafting ineffective unless the condition is stabilized first.
Ignoring these signs can delay treatment and lead to complications. Consulting with a periodontist is vital to determine whether gum grafting is still a viable option for your oral health.
Factors That Influence the Success of Gum Grafting
Several factors impact whether gum grafting will be successful or if alternative treatments are necessary.
1. Age and Overall Health
While age itself isn’t a strict barrier, younger patients often have healthier gum tissue and better healing capacity. Older patients or those with systemic conditions like diabetes or autoimmune diseases may experience slower recovery or complications, making timely intervention essential.
2. Gum Health and Tissue Availability
The availability of healthy tissue for grafting significantly influences outcomes. In cases of severe gum recession, there may not be enough healthy gum tissue to perform the procedure. In such cases, alternative grafting methods or synthetic materials may be considered.
Being proactive about gum care and addressing recession early increases the chances of successful grafting. Regular dental checkups and early intervention are key to maintaining your eligibility for this procedure.
Alternative Treatments When Gum Grafting Is Not an Option
If gum grafting is no longer feasible, don’t lose hope—other treatments may be available.
1. Bone Grafting and Tissue Regeneration
Bone grafting can rebuild lost bone tissue, laying the foundation for future gum grafting. Regenerative procedures, such as guided tissue regeneration, use membranes and proteins to encourage new growth, creating a stable environment for further intervention.
2. Dental Implants and Prosthetics
For individuals with severe gum and tooth loss, dental implants or prosthetics may offer a long-term solution. Implants can restore function and aesthetics while preventing further bone deterioration.
Discussing your options with a dental professional ensures you receive the most suitable treatment plan, even if gum grafting isn’t viable.
How to Prevent Gum Recession and Prolong Gum Health
Prevention is always better than cure, and maintaining gum health is the best way to avoid the need for invasive procedures.
1. Maintain Excellent Oral Hygiene
Brushing twice daily with a soft-bristled toothbrush and using fluoride toothpaste can prevent gum recession. Don’t forget to floss daily and consider using an antibacterial mouthwash to keep your gums healthy.
2. Regular Dental Checkups
Visiting your dentist every six months helps catch gum issues early. Professional cleanings remove plaque and tartar, which contribute to gum disease, while early detection ensures timely intervention.
Lifestyle changes, such as quitting smoking and managing stress, can also significantly impact gum health. Being proactive about your oral care can reduce the likelihood of needing gum grafting in the future.
Conclusion
When is it too late for gum grafting? The answer depends on the extent of gum and bone damage, as well as overall oral health. Early diagnosis and intervention are critical to ensuring the success of gum grafting. If your condition has progressed beyond what gum grafting can address, alternative treatments like bone grafting or implants can still offer hope. Consulting with a qualified dental professional will help you navigate your options and make informed decisions about your oral health.
FAQs About When It’s Too Late for Gum Grafting
- What is the success rate of gum grafting?
Gum grafting has a high success rate, typically over 90%, especially when performed early. - Can gum grafting fail?
Yes, failure can occur due to infection, improper healing, or inadequate tissue support. - How do I know if I need a gum graft?
Signs include gum recession, tooth sensitivity, and visible roots. Consult a dentist for confirmation. - Can advanced gum disease be reversed?
While advanced gum disease cannot be fully reversed, treatments can manage the condition and prevent further damage. - What happens if I don’t treat receding gums?
Untreated gum recession can lead to tooth sensitivity, decay, bone loss, and eventually tooth loss. - How long does it take to recover from gum grafting?
Recovery typically takes 1-2 weeks, though full healing may take up to a few months. - Is gum grafting painful?
The procedure is usually performed under local anesthesia, and discomfort can be managed with prescribed medication. - Are there alternatives to traditional gum grafting?
Yes, options like allografts or synthetic materials are available for patients without sufficient donor tissue. - Does insurance cover gum grafting?
Coverage depends on your insurance plan and the reason for the procedure. Check with your provider for details. - How much does gum grafting cost?
Costs vary based on the severity of gum recession and the number of grafts needed, ranging from $600 to $1,200 per graft.